Diabetic and Neuropathic Ulcers
Diabetic and Neuropathic Ulcers
See how you can benefit from advanced, comprehensive treatment for diabetic and neuropathic ulcers at Innovative Wound Care Specialists.
Diabetic and neuropathic ulcers occur when a person cannot feel an injury to the area. High blood sugar levels and nerve damage can cause this loss of feeling.
Diabetic and neuropathic ulcers are chronic wounds that occur when a person cannot feel the injury. Oftentimes, those with severe diabetes may form these ulcers on their feet. The ulcers stem from a combination of peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage), poor circulation, and repetitive pressure over time, such as shoes rubbing against the feet.
Left untreated, these ulcers often lead to serious complications. Neuropathic ulcer specialists at Innovative Wound Care are here to help.
Start Treatment Today
Peripheral neuropathy refers to a condition characterized by the damage or degeneration of peripheral nerves. These are the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, serving as communication links between the central nervous system and the rest of the body.
This condition can be further categorized into three main types:
Sensory Neuropathy
- Symptoms: It primarily affects the sensory nerves, leading to a loss of sensation. Individuals may become unable to feel pain or pressure, a condition often referred to as the loss of protective sensation (LOPS).
- Impact: This loss can increase the risk of injuries because warning signals like pain are no longer effective.
Motor Neuropathy
- Symptoms: This type involves damage to motor nerves, which control muscles and movement.
- Impact: Sufferers may experience weakened muscles, leading to claw-like toe deformities and, eventually, conditions such as foot drop, where the individual has difficulty lifting the front part of the foot.
Autonomic Neuropathy
- Symptoms: The autonomic nerves are affected, which are responsible for involuntary bodily functions.
- Impact: This can result in the inability to produce sweat and oils, leading to dry and less elastic skin, which can cause additional skin issues.
Understanding these types helps in identifying the symptoms and potential risks associated with peripheral neuropathy, allowing for better management and treatment of the condition.
For those living with diabetes and neuropathy, the risk of developing foot ulcers is a constant concern. Neuropathy can dull sensations in the feet, so minor injuries may go unnoticed and untreated for an extended period of time, often becoming worse. Poor blood circulation further complicates the healing process, as it increases the likelihood of infection and more severe outcomes, including amputation.

When an individual loses sensation on a part of their body due to neuropathy, spinal cord injury, or diabetes, detecting a wound or an ulcer can be difficult. Those at risk of ulcers should have their feet checked regularly for cracks, cuts, blisters, or other wounds.
Symptoms of ulcers include:
Visible Wounds: The most obvious sign is an open sore or wound on the foot, typically on the bottom of the feet, toes, or heels. These wounds may excrete fluid or pus, which can show up as stains on socks or shoes.
Redness, Swelling: The area around the ulcer may become red and inflamed. If the skin is swollen and warm to the touch, the ulcer is likely infected.
Pain and Changes in Sensation: Ulcers may be painful, especially when infected. However, due to neuropathy, some individuals may not feel any pain despite having serious ulcers. Furthermore, neuropathy can cause numbness or tingling in the feet, which can mask any pain from ulcers.
Unpleasant Odor: A persistent, foul odor from the ulcer often indicates infection or necrotic tissue.
Fever and Chills: Systemic signs of infection can include fever, chills, and malaise.
Calluses: There may be hard, thickened skin around the ulcer caused by repeated pressure and friction.
Red Streaks: Red streaks extending from the ulcer suggest a more serious infection, such as cellulitis.
Non-Healing Wound: A wound that does not show signs of healing over several weeks, despite wound care, may indicate an underlying diabetic ulcer.
Diabetic and neuropathic ulcers are significant complications of diabetes, affecting millions of people worldwide. Understanding the causes of diabetic and neuropathic foot ulcers is crucial for several reasons. It aids in early detection, effective prevention, targeted treatment, patient education, and ultimately improves patient outcomes.
Here are several causes:
- Nerve Damage
Diabetes can cause peripheral neuropathy, leading to loss of sensation in the feet. This makes it difficult for individuals to notice injuries, cuts, or blisters, which can develop into ulcers. - Muscle Weakness
Nerve damage can also lead to muscle weakness and imbalance, altering the foot’s shape and increasing pressure points, which can cause ulcers. - Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Diabetes often leads to PAD, which reduces blood flow to the extremities. This poor circulation impairs wound healing, making ulcers more likely to form and difficult to heal. - Microvascular Complications
Damage to the small blood vessels (microangiopathy) also contributes to poor circulation and delayed wound healing. - Bunions, Hammertoes, and Charcot Foot
These foot deformities can cause abnormal pressure points on the foot, leading to skin breakdown and ulcer formation. - High Blood Sugar Levels
Elevated blood sugar levels can impair the immune response, increase infection risk, and reduce the body’s ability to heal wounds. - Minor Injuries
Cuts, scrapes, and burns can go unnoticed due to neuropathy and develop into ulcers. - Pressure and Friction
Repetitive stress from ill-fitting shoes or constant pressure on certain foot areas can lead to skin breakdown and ulcer formation. - Inadequate Foot Care
Lack of regular foot inspections and proper foot hygiene can contribute to ulcer development and progression.
Given the high prevalence and severe complications associated with diabetic and neuropathic ulcers, early intervention, regular monitoring, and comprehensive care are crucial. Please see a neuropathic ulcer specialist if you are experiencing any of these symptoms and you have diabetes or neuropathy.
For individuals managing diabetes, choosing the right footwear is crucial. A well-fitted shoe plays a significant role in maintaining foot health and offers several essential benefits:
- Support Throughout Movement: The ideal shoe ensures stability and balance during each step, reducing the risk of slips and falls.
- Foot Protection: It guards the foot against injuries, blisters, and sores, which can be particularly problematic for diabetic patients due to slower healing processes.
- Pressure Distribution: Proper footwear helps in evenly distributing pressure across the foot, preventing excess strain on vulnerable areas.
- Enhanced Comfort: A snug fit reduces friction and discomfort, minimizing the risk of rubbing and chafing that could lead to complications.
Taking care of your feet daily is crucial in preventing ulcers. Here are some effective practices to incorporate into your routine:
- Inspect Your Feet Regularly: Use a mirror to check the soles of your feet for any cuts, blisters, or abnormalities.
- Nail Maintenance: Trim your nails straight across or gently file them to prevent ingrown nails or injuries.
- Always Wear Proper Footwear: Avoid walking barefoot. Even when indoors, opt for shoes instead of thin-soled slippers or just socks. Choose footwear that is comfortable and well-fitting, avoiding any with rough edges or seams that might irritate your skin.
- Socks and Stockings: Wear seam-free socks or turn seams inside out to minimize friction. Avoid tight or knee-high socks unless prescribed, and remember to change them daily.
- Hygiene and Moisture: Clean your feet daily using water that’s comfortably warm, but never hot, to avoid burns. Dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes. Instead of heaters or hot-water bottles, opt for socks to keep your feet warm.
- Avoid Harsh Treatments: Do not attempt to remove corns or calluses with chemical agents. Consult a healthcare professional for safe and effective treatment. To prevent dry skin, apply emollients, but steer clear of applying them between the toes to avoid trapping moisture.
- Professional Care: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can catch potential issues early and provide guidance tailored to your needs.
It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you notice any signs of a foot ulcer, especially if you have diabetes. Early intervention can prevent complications such as infection, gangrene, and amputation. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, proper foot care, and managing diabetes are essential for preventing and treating diabetic and neuropathic foot ulcers.
Effective management and care planning for diabetic foot ulcers involve a multi-faceted approach:
- Diabetes Management: Optimize blood glucose levels and manage co-morbidities like blood pressure and lipids. Consider psychosocial factors and seek interventions such as nutritional assessments and smoking cessation programs.
- Foot Care: Identify the ulcer’s cause and address factors like inappropriate footwear or foot trauma. Regular foot screenings and patient education on self-care—such as daily foot checks and avoiding barefoot walking—are vital.
- Ulcer Assessment: Conduct thorough wound assessments to tailor a treatment plan that maintains moisture balance and reduces bacterial load.
- Vascular Health: Assess blood flow and consult specialists if necessary to ensure adequate circulation for healing.
- Infection Control: Monitor for signs of infection, obtain necessary cultures, and choose appropriate antibiotics and antimicrobials as needed.
- Pressure Management: Use offloading devices to reduce pressure on the ulcer, considering the patient’s lifestyle and needs. Non-weight-bearing strategies like crutches or wheelchairs might also be suitable.
- Sharp Debridement: Remove calluses and necrotic tissue to decrease pressure and bacterial reservoirs.
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of a diabetic or neuropathic ulcer, contact Innovative Wound Care Specialists today to schedule a wound assessment and personalized treatment plan.
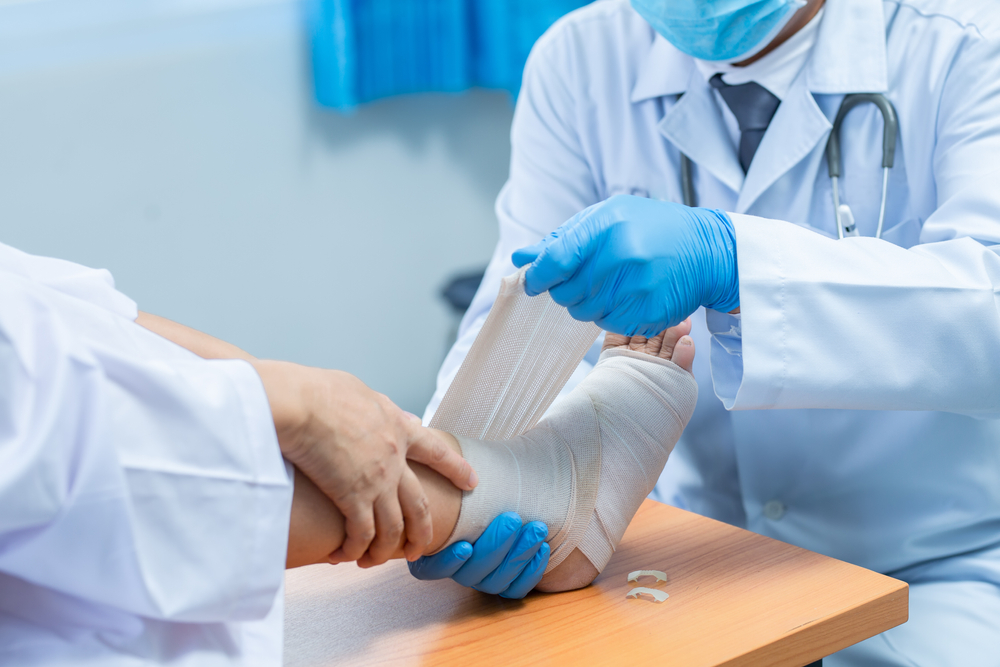

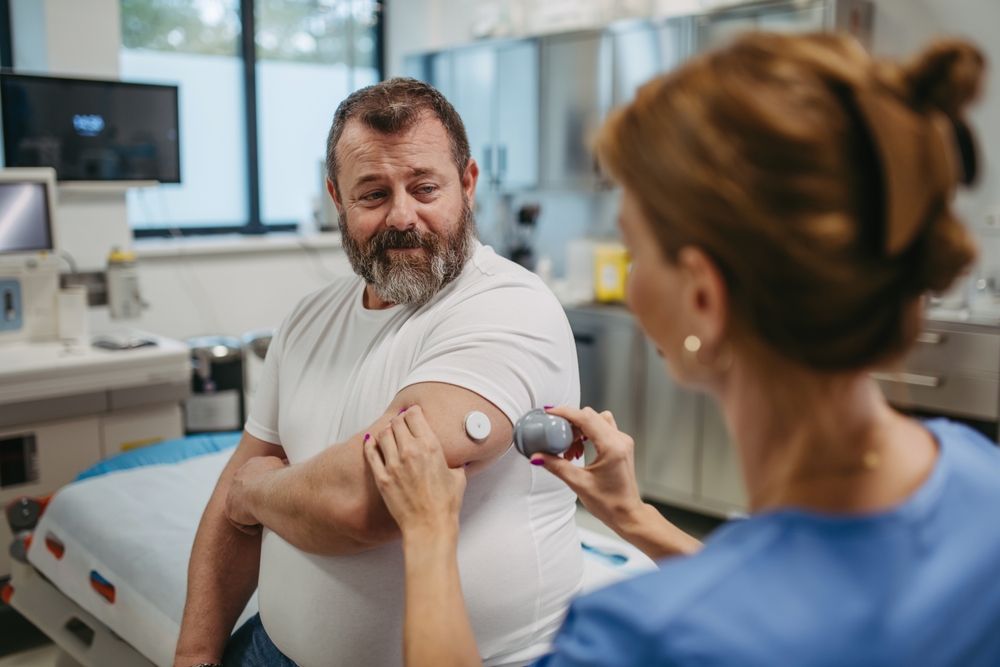
Patient and wound assessments are essential components of the wound care process, playing a crucial role in understanding the patient’s overall health, identifying factors that may impact wound healing, and tailoring an effective treatment plan.
Assessing the patient’s overall health, medical history, and lifestyle factors helps healthcare professionals at IWC understand potential underlying conditions that may affect wound healing. Factors that may affect wound healing include diabetes, vascular disease, nutritional status, and immune function.
At Innovative Wound Care Specialists, we provide a comprehensive range of advanced treatments to promote effective wound healing and enhance overall well-being. From Compression Dressings to Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), our services address various wound types and underlying conditions.
Our goal is to deliver advanced treatments and compassionate care for every patient’s unique needs to promote long term healing and prevent recurrence with the help of our professional wound specialists.
Chronic wounds can cause patients to suffer and affect mobility. While most wounds heal quickly, chronic ulcers may not heal or fail to improve for weeks and can cause severe problems if left untreated.
Wound Care May Include . . .
Compression Dressings & Advanced Wound Dressings – We offer a variety of innovative wound dressings, including those with antimicrobial properties, moisture control, and pressure relief features.
Laboratory and Vascular Evaluation – Monitor patient’s peripheral artery disease (PAD) and its effect on supplying blood to wounded tissues.
Cellular or Tissue-Based Products – Utilizing bioengineered skin grafts and substitutes to promote faster healing and tissue regeneration.
Wound Measurement and Photographs – To monitor wound progression and wound healing.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) – Enhancing oxygen supply to the affected area to accelerate wound healing and combat infection.
Surgical Procedures and Support – Assisting in wound closure, infection control, tissue removal or repair, promotion of granulation tissue, reducing tension on wounds, enhancing blood supply, and management of complications.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT) – Using controlled suction to remove exudate, reduce edema, and improve blood flow to the wound.
Prosthetic and Pressure Relief Assistance – To reduce pressure on the ulcer, we provide specialized footwear and custom orthotics, designed to redistribute weight and minimize friction.
Debridement – Removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue by surgical or other means to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue.
How Does Loss of Sensation Affect the Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
When evaluating and treating diabetic foot ulcers, the loss of sensation plays a critical role in both the diagnosis and management, as loss of sensation can prevent a patient from seeking a medical diagnosis if everything seems or feels normal.
Diagnosis Implications
Delayed Detection: Due to diminished sensation, patients may not notice injuries or pressure points that lead to ulceration. This can cause delays in seeking treatment until more severe symptoms appear.
Severity Assessment: Neuropathy makes it challenging to assess the severity of the ulcer based solely on patient-reported symptoms, necessitating thorough medical examination and diagnostic imaging when needed.
Management Strategies
Regular Monitoring: Frequent foot inspections by healthcare providers are essential to identify changes or deterioration in the condition early on.
Pressure Offloading: Special footwear or devices, like orthotic shoes, are recommended to redistribute pressure away from the ulcer site, aiding in healing.
Wound Care Protocol: Proper debridement of callus and necrotic tissue surrounding the ulcer is crucial. Ensuring a moist wound environment and applying appropriate dressings can facilitate healing.
Patient Education: Educating the patient about daily foot care routines, such as checking for signs of injury and avoiding walking barefoot, is imperative to prevent further complications.
What Role Does the Presence or Absence of Foot Pulses in an Ulcer Play?
When evaluating diabetic foot ulcers, assessing foot pulses is crucial. Foot pulses provide insight into the blood flow reaching the feet. Normal foot pulses suggest adequate circulation, which is essential for healing and helps distinguish neuropathy from vascular issues.
In cases where foot pulses are absent or weak, it may indicate peripheral artery disease (PAD), which can complicate ulcer healing due to reduced blood supply.
Ultimately, evaluating foot pulses assists in diagnosing the underlying causes of ulcers and directing appropriate treatment strategies.
At Innovative Wound Care Specialists, our professional neuropathic ulcer specialists are dedicated to transforming lives through expert wound care and advanced treatments for diabetic and neuropathic ulcers in Flint, Michigan.
If you or a loved one is struggling with a diabetic or neuropathic ulcer, don’t wait for the condition to worsen. Contact Innovative Wound Care Specialists today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards effective, comprehensive wound care. Your journey to healing starts here.
Contact us by phone (810) 600-2030 or email info@innovativewoundspecialists.com and our friendly staff will assist you every step of the way. Don’t wait any longer—get started today! We’re here to help.
